BREAST PTOSIS (SAGGING): CAUSES AND CLASSIFICATION
For most women, breast sagging is a serious aesthetic problem that interferes with loving your own body and causes complexes, so the question of treating breast ptosis is especially important.
Involutionary aging processes, a genetic predisposition, and the every minute effect of the Earth's gravitational forces contribute to the natural ptosis of the skin, body tissues, and some internal organs.
With ptosis, a woman's breast loses its elastic shape and looks saggy. Special preventive care only helps to slow down the process of breast ptosis. It includes: contrast shower, massages, body wraps, cosmetics, mesotherapy, biorevitalization of the skin of the chest, as well as some other salon procedures. However, with severe ptosis, conservative methods are no longer effective.
Causes of breast ptosis:
The volume and appearance of the female breast is determined by the condition of the pectoralis major muscle and ligaments, the ratio of adipose and glandular tissue formed in lobules.
- Age-related changes. Over time, the breast tissues stretch out by their own weight, the muscles of the breast lose their tone, the volume of the glandular tissue decreases. As a result, the mammary glands settle down and lose their elasticity.
- Genetic factor - congenital features of the synthesis of collagen and elastin determine the rate of tissue aging and predisposition to gigantomastia, and therefore to ptosis.
- Pregnancy and lactation period. During pregnancy, the mammary glands increase significantly in size due to hormonal changes and weight gain. In case of increase of glandular tissues and fatty layer, muscles and skin are stretched out. At the end of the lactation period, when the weight and the endocrine profile balance back, the size returns to the original one, and the muscles and skin cannot regain their tone by themselves.
- Big size. If by nature or as a result of plastic surgery the breast is too large, which does not correspond to the woman's complexion, this can lead to early ptosis.
- Rapid weight loss or weight gain. Adipose tissue not only actually determines the shape of the mammary glands. In the case of rapid weight loss, part of the breast volume is lost, and the skin does not have time to recover. In adipocytes of adipose tissue, hormones that are responsible for metabolism are stored and synthesized. On the contrary, rapid weight gain leads to an increase in the volume of the mammary glands and stretching of the skin.
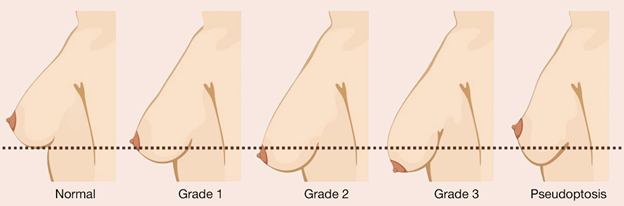
Degrees of Breast Ptosis:
Grade 1 – Mild: the initial stage of breast ptosis, in which the nipple is at the level of the submammary (pectoral) fold or slightly lower.
Grade 2 – Mild to moderate: when the center of the areola is close to 3 cm below the inframammary crease.
Grade 3 – Severe: If the central point of areola is more than 3 cm below the crease level.
Pseudoptosis: Pseudo-ptosis occurs when the nipple is still above the inframammary crease, but the breast appears to droop because of a large, flattened breast lobe.
Parenchymal maldistribution involves a lack of fullness in the lower portion of the breast, a high inframammary fold and a relatively short distance from the fold to the nipple, seen in conditions such as a tuberous breast.
Some women with ptosis choose to undergo plastic surgery to make their breasts less ptotic. Plastic surgeons offer several procedures for lifting sagging breasts. Surgery to correct the size, contour, and elevation of sagging breasts is called mastopexy. Women can also choose breast implants, or may undergo both procedures. The breast-lift procedure surgically elevates the parenchymal tissue (breast mass), cuts and re-sizes the skin envelope, and transposes the nipple-areola complex higher upon the breast hemisphere. If sagging is present and the woman opts not to undergo mastopexy, implants are typically placed above the muscle, to fill out the breast skin and tissue. Submuscular placement can result in deformity. In these cases, the implant appears to be high on the chest, while the natural breast tissue hangs down over the implant.
Correction of breast ptosis with the Los Deline® injectable implant is possible in case of ptosis of 1-2 grades. In grade 3 ptosis when the breast ligamentous apparatus is severely stretched, it is impossible to obtain fully proper aesthetic result because skin elasticity will be kept partially. In cases of some mammary gland malformations like lower pole breast constriction or tubular breast deformity, it is impossible to give the breast tear-shaped form. I this cases breast lift or mastopexy are preferable.